Technology
Subnet Conceptual Network Architecture
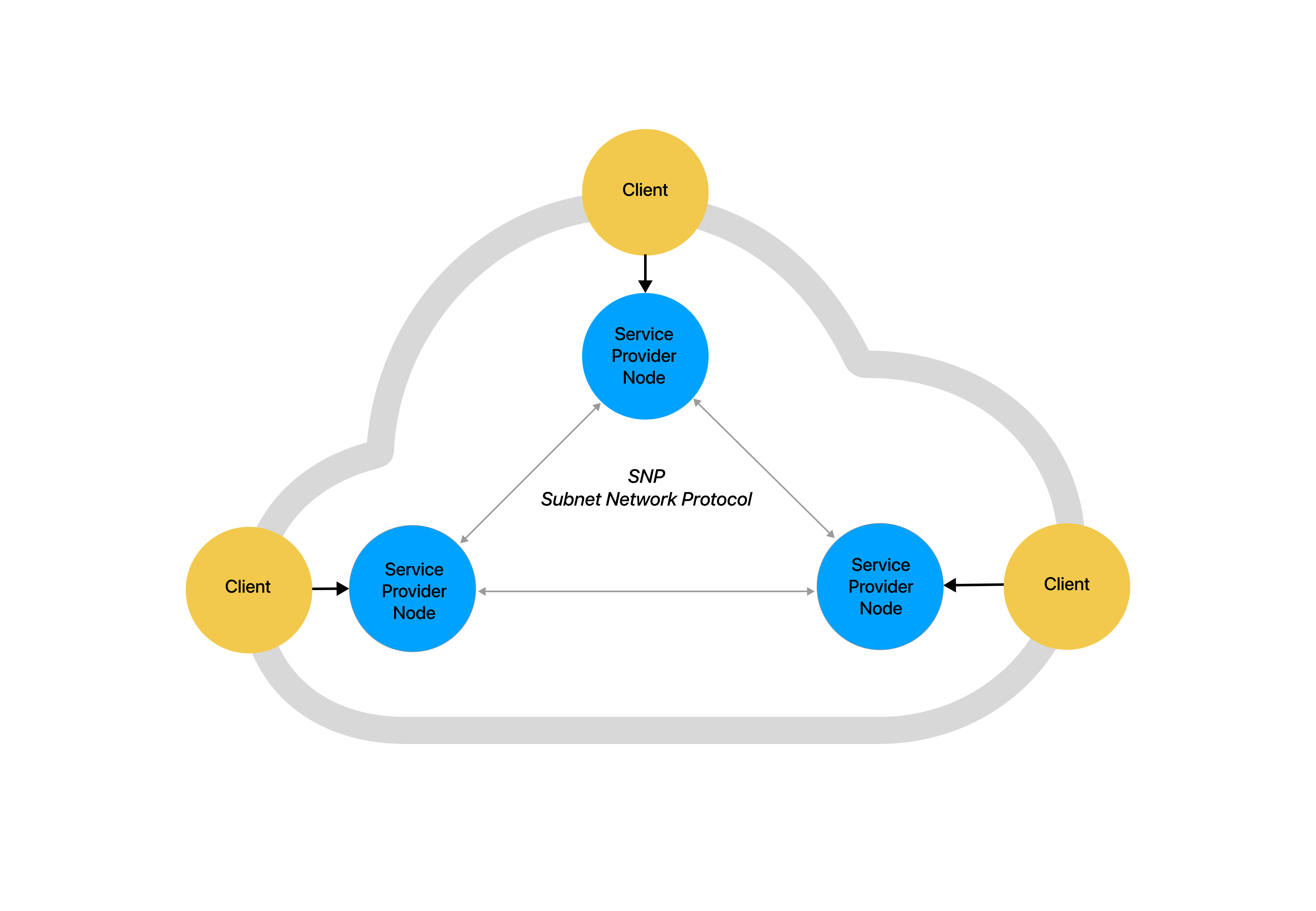
Network Entities
The platform includes 5 main distinct network entities:
- Service Providers p2p Nodes
- Service Bootstrap p2p Nodes
- Subnet blockchain p2p Nodes
- Client Apps
- Bootstrap p2p Nodes
Service Providers Nodes
Service Providers nodes are servers running a release of Subnetter - the Subnet p2p software for service providers. Service providers nodes must be online 24x7 and IPV4 or IPV6 Internet-routable, so they can receive incoming connections from clients and other nodes over the Internet.
Service providers do not have access to any content sent or received on the network between users. Users are able to verify the authenticity and security of messages sent on the network without having to trust providers nodes.
Service Providers Nodes are designed enable any two users to exchange data in higher-level communication protocols under the assumptions that user's client software is non-routable and often offline.
Client software apps operated by users connect to providers nodes in order to send and receive messages. Subnet is designed to support non-routable and often offline clients. Provider nodes provide the federated backbone of the Subnet network. Providers nodes route messages to their users sent from other nodes.
As part of routing, providers nodes store users messages on a temporary ttl-based basis, and forward user messages to other nodes when a user's client goes online and sends a request for messages designated to it.
Service Providers node also store encrypted user data that enable users to easily migrate from client to client and to migrate their account to another service provider.
The Subnet Blockchain
Each Service Provider entity runs at least one SUB blockchain p2p node. These nodes run a blockchain p2p protocol between them and reach agreement on an immutable global shared state via a consensus protocol. Service Providers nodes are configured to use a blockchains node for cryptocurrency, identity and other Subnet data functionality. The Subnet blockchain maintains users' and providers' coin accounts balances, identity bundles and providers' service terms.
It supports the core $SUB cryptocurrency and $SST, Subnet's stable token. The Subnet blockchain is a globally replicated database that is updated by an honest majority of Subnet blockchain nodes. Anyone, without limitation, can run an SUB blockchain node and provide the 'Blockchain Service' to the network. In other words, the Subnet Blockchain is permissionless.
Bootstrap Nodes
Bootstrap nodes are custom service providers nodes which are configured to provide public Subnet APIs to anyone. Bootstrap nodes do not provide non-public user-specific APIs as they do not provide specific network services to end-users. These are provided by service providers nodes. The public Subnet APIs enable users to locate service providers and to obtain data from the Subnet blockchain such as providers coin balances, users coin balances, users identity and providers identity.
Using a bootstrap node, any identity can find the identity of any entity on the network and update its identity bundle it shares on the network at any time. Bootstrap nodes are a public utility on the Subnet network and will be operated by the Subnet Dao as a community service.
Using bootstrap nodes, users can locate available service providers to provide them with network services.
Clients
The client is a software application used by people to use network services provided on the Subnet platform. We foresee web-based clients, native desktop clients and mobile native clients.
Clients provide the user interface for the applications provided on the platform and include a wallet that maintains user private keys and enables users to sign transactions, messages and other commitments.
Clients are not required to be Internet-routable, they only need to be able to connect to their service provider's node. Providers nodes may provide a websocket connection for clients, others may provide a json/http or a grpc endpoint. Clients can be honest or byzantine. Honest Clients implement the Subnet public protocols and APIs and Byzantine Clients do not. This concept is used in the Subnet security analysis.
Subnet Technology Overview
Subnet integrates four fundamental decentralization technologies to deliver the platform's design goals.
A
Blockchain Sericeused for name resolution and network services discovery, implemented using a permissionless blockchain.A blockchain-style
consensus protocolover a cryptocurrency ledger with built-in support to a small and well-defined set of transaction types, anative cryptocurrencyand adecentralized stable coin.A modern
p2p messaging protocolbuilt on top of core Internet protocols supporting authentication, encryption, custom app-level protocols and both push and pull models of communications. The p2p protocol uses aX3DH-like protocolwe callX2DHfor async, ephemeral key exchange and authentication we adapted to a server-less decentralized context. Learn more about [X3DH]((https://signal.org/docs/specifications/x3dh/).The p2p protocol makes extensive use the
Double Ratchetencryption algorithm to secure communications on the platform.
Subnet replaces centralized managed network servers used in legacy internet service provisioning, with decentralized and incentivized full p2p nodes which provide network services to end-users. The Subnet native cryptocurrency is used to incentivize servers on the network to achieve consensus on the cryptocurrency ledger.
Building Blocks
Subnet Blockchain
Subnet blockchain nodes run a distributed consensus protocol and agree on a canonical ledger between them. The simple ledger includes identity bundles, accounts $SUB coin and token balances. The ledger is where $SUB coin balances settle. For example, clients deposit funds to service providers by sending $SUB coin to provider's blockchain account via a blockchain transaction and periodical users bills are settled on the SUB blockchain.
Account Model
An account model is more appropriate for the subnet blockchain instead of UTXO model.
TODO detail support for
hash-locked accounts- enabling the priority inbox app and deposits.
Proof of Useful Work (PoUW)
Subnet blockchain nodes use proofs of useful work (PoUW) when deciding how to act on messages that only other service providers send them according to SUB. This helps spam prevention, storage waste and protocol abuse. Proof of useful work can be easily verified with on-chain data that provides evidence of good behavior and work according to the Subnet blockchain consensus protocol - e.g. blocks production, participation in consensus protocol over a period of time, and getting coin awards for honest useful behavior. In other words, service providers must run Subnet blockchain nodes and prove that to other providers when sending messages to them.
The X2DH Protocol
Employed between 2 entities to exchange public keys used for creating shared secrets between entities which are further used to secure communications between entities.
We chose to use X2DH over X3DH as X3DH leaks message senders identity. X2DH enables receiver to authenticate sender without leaking sender's identity to other entities.
The Double Ratchet Algorithm
We employ a modified version of the Double Ratchet algorithm to create secure communications channel between any to entities on the SUB network. Two entities use a 2XDH generated shared secret to create three chains of encryption keys which are used to secure messages between them: a root-chain, a-send chain and a receive-chain. In addition, message headers are encrypted using header encryption.